All About Earwax
Understanding Earwax
Essential ear health information for better hearing and comfort
Earwax is perfectly normal and essential for ear health. But when it builds up, it can affect hearing, comfort, and quality of life—especially for older adults, care home residents, and hearing aid users.
This guide explains everything you need to know about earwax: what it is, why it varies, when it becomes a problem, and how professional care can help.
Earwax (cerumen) isn't just debris—it's a sophisticated protective system produced by your ear canal. It's a mixture of oils, dead skin cells, and secretions that work together to keep your ears healthy.
How Earwax Protects You
- Traps dust, bacteria, and foreign particles before they reach your sensitive eardrum
- Keeps your ear canal lubricated and prevents dry, itchy, irritated skin
- Provides antibacterial protection through natural enzymes that prevent infections
- Naturally migrates outward as part of your ear's self-cleaning process
In a healthy ear, wax moves from the inner ear canal outward through jaw movement and natural skin migration, carrying trapped particles with it. This process happens at roughly the same rate your fingernails grow—about 1mm per month.
When the system breaks down: As we age, ear canals can narrow. Hearing aids block the natural migration path. Cotton buds push wax deeper. That's when professional care becomes necessary.
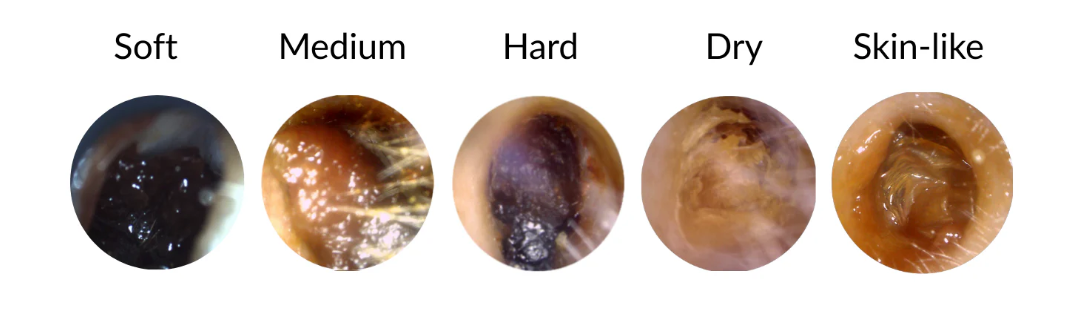
Your earwax type is determined by genetics—specifically, a gene called ABCC11. Understanding your type helps you know your ear care needs.
Wet Earwax
Appearance: Sticky, golden or yellowish-brown—similar to honey or soft caramel.
Who has it: Most common in people of European and African descent.
Key characteristics:
- Higher fat and pigment content
- More likely to build up and cause blockages
- May require professional removal more frequently
- Can sometimes have a mild odour
Dry Earwax
Appearance: Flaky, dry, and light-coloured—often greyish or pale yellow.
Who has it: Most common in people of East Asian and Native American descent.
Key characteristics:
- Crumbly, brittle texture
- Less likely to cause impacted blockages
- Often clears naturally through jaw movement
- May still require removal if compacted
While earwax is beneficial, excessive buildup can significantly impact daily life—especially for older adults, hearing aid users, and care home residents.
⚠️ Signs You Need Professional Ear Care
- Muffled or reduced hearing — often gradual and mistaken for hearing loss
- Ear discomfort, fullness, or pressure
- Tinnitus (ringing, buzzing, or humming sounds)
- Itching or irritation in the ear canal
- Dizziness or balance issues (in severe cases)
- Hearing aid feedback or poor performance
- Pain or discharge (seek medical attention immediately)
The Real Impact on Quality of Life
Earwax buildup isn't just uncomfortable—it can lead to:
- Social isolation — Missing conversations with family and friends
- Safety risks — Not hearing alarms, doorbells, or traffic
- Cognitive decline concerns — Untreated hearing loss is linked to faster cognitive decline
- Reduced independence — Difficulty using phones, watching TV, participating in activities
- Hearing aid ineffectiveness — Expensive devices rendered useless by wax buildup
Most ears are self-cleaning, but when problems arise, the approach depends on severity and your individual circumstances.
At-Home Care (For Mild Cases)
What works:
- Over-the-counter olive oil or sodium bicarbonate ear drops
- Apply 2-3 drops twice daily for 3-5 days to soften wax
- Clean only the outer ear with a washcloth
- Tilt head to allow drops to penetrate
What to NEVER do:
- ❌ Cotton buds or Q-tips (push wax deeper, risk perforation)
- ❌ Bobby pins, paperclips, or other objects
- ❌ Ear candles (dangerous and ineffective)
- ❌ High-pressure water syringes without training
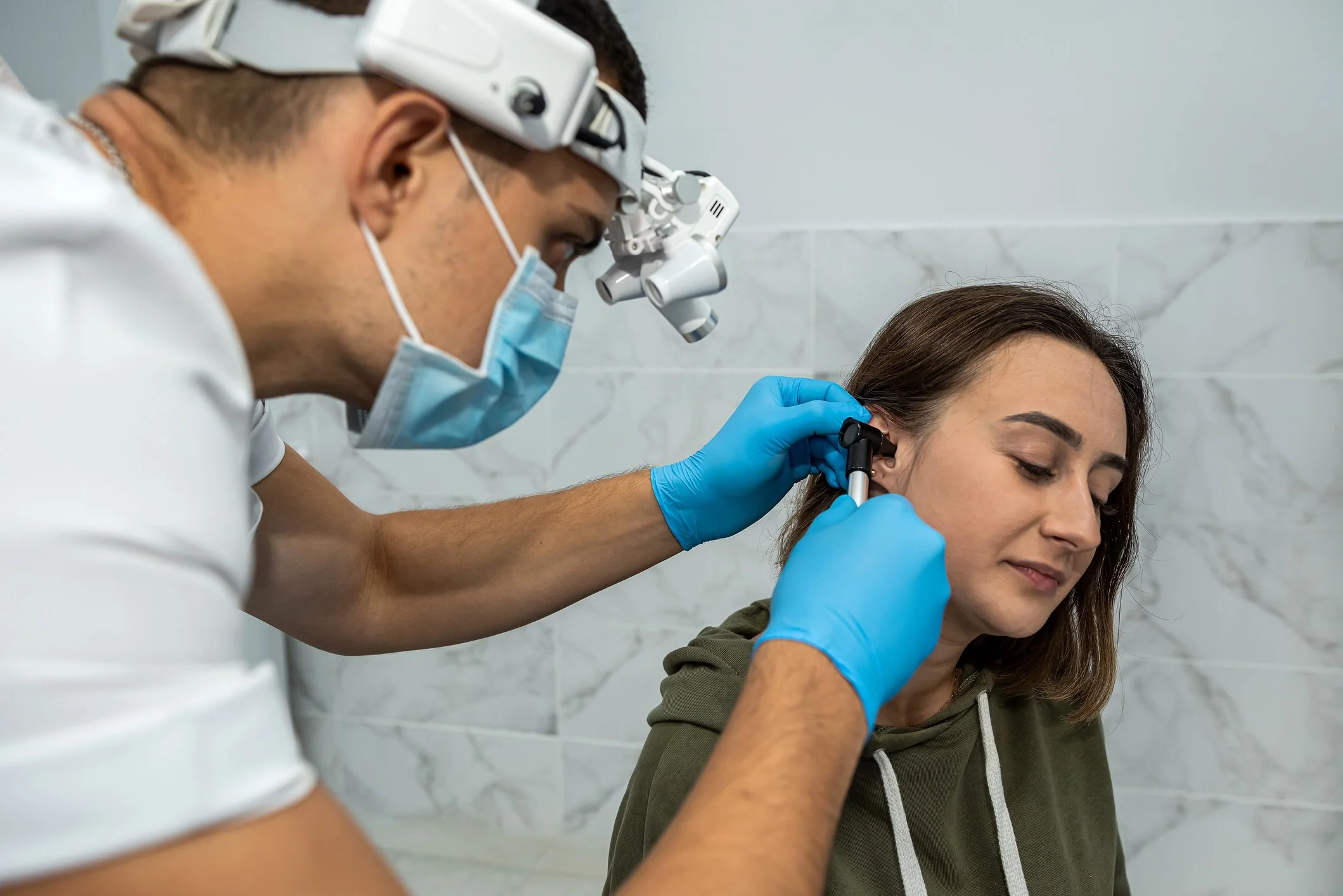
Professional Removal (Safe, Effective, Immediate Relief)
We provide three evidence-based methods, chosen based on your specific needs:
1. Microsuction — Gentle vacuum removal under direct vision using a medical-grade suction device and microscope or video otoscope. Safest method for perforated eardrums or previous ear surgery.
2. Irrigation — Controlled warm water flushing using specialized equipment to gently flush wax out. Effective for large, soft blockages.
3. Manual Instrumentation — Precise removal with specialized tools under direct vision. Ideal for hard, compacted wax or when other methods aren't suitable.
All treatments include video otoscopy so you can see your ear canal before and after on a monitor. This ensures transparent, informed care.
Why Choose Professional Care?
- Direct visualization — We see exactly what we're treating in real-time
- Complete removal in a single appointment—no waiting days for drops to work
- Safety for complex cases: narrow ear canals, previous surgery, perforations, infections
- Immediate relief from hearing loss and discomfort
- Detection of underlying conditions that may need medical attention
- Mobile service — We come to you (home, care facility, workplace)
The NHS Ear Care Gap
Many GP surgeries and NHS services have reduced or stopped offering earwax removal. This leaves thousands of people—particularly older adults and care home residents—without access to essential ear care.
The impact:
- Months-long waiting lists for the few NHS services still available
- Care home residents going years without ear checks
- Hearing aids sitting unused due to wax buildup
- Preventable hearing loss affecting quality of life
Clear Ear Cheer Fills the Gap
We provide accessible, professional ear care across Essex and Suffolk with:
- Mobile service — We come to you, eliminating travel barriers
- Care home partnerships — Regular visits, bulk appointments, coordinated care
- Affordable pricing — Transparent rates, no hidden costs, supportive pricing for care sector
- Clinical expertise — HCPI-trained, fully insured, Enhanced DBS checked
- Medical coordination — GP and ENT referrals when concerns extend beyond earwax
Fascinating Earwax Facts
- Your earwax composition is as unique as a fingerprint—forensic scientists can use it for identification
- Earwax migrates outward at roughly the same rate your fingernails grow (about 1mm per month)
- Whale earwax builds up in layers like tree rings—scientists use it to study whale age and environmental exposure throughout their lifetime
- In ancient medicine, earwax was used as a lip balm and to treat wounds (though we don't recommend this!)
- Stress and anxiety can increase earwax production in some people
- The smell and consistency of earwax can indicate certain genetic conditions or health issues
- Earwax contains natural antibiotics that kill bacteria—it's your ear's first line of defense
Experiencing Hearing Difficulties or Ear Discomfort?
Professional ear care can often restore your hearing and comfort in a single appointment.
Mobile service across Essex, Suffolk, and parts of London
Book Your AppointmentOr call 07534 764560 to discuss your needs
Important: For concerns beyond earwax removal—such as persistent pain, sudden hearing loss, or discharge—please consult your GP, ENT specialist, or audiologist for personalized medical care. Visit NHS.uk for more health information.